
|
КОНСПЕКТЫ ЛЕКЦИЙ, ШПАРГАЛКИ
Английский язык для медиков. Cell (конспект лекций)
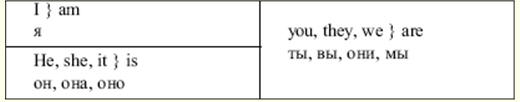
Справочник / Конспекты лекций, шпаргалки Оглавление (развернуть) ЛЕКЦИЯ № 1. Cell The cell is a smallest independent unit in the body containing all the essential properties of life. types of human cells can be grown in test tubes after beeing taken from the body. Cells which are functionally organized are often grouped together and operate in concert as a tissue, such as muscle tissue or nervous tissue. Various tissues may be arranged together to form a unit called organ as the kidney, liver, heart or lungs. Organs often function in groups called organ systems. Thus the esophagus, stomach, раnсreаs, liver and intestines constitute the digestive system. Cells are characterized Ьуг high degree of complexity and order in both structure and function. The cell contains a number. Of structures called cell organelles. These are responsible for carrying out the specialized biochemical reactions characterizing each. The many chemical reactions taking place in a cell require the establishment of varied chemical microenvironment. Carefully controlled transport mechanisms along with highly effective barriers - the cell membranes - ensure that chemicals are present in the proper region of the call in appropriate concentration. The cell membranes of a mixture of protein and lipid form its surroundings. Membranes are an essential component of almost all cells organel-les. The membrane allows only certain molecules to pass through it. The most visible and essential organelle in a cell is the nucleus, containing genetic material and regulating the activities of the entire cell. The area outside of the molecules is called the cytoplasm. Cytoplasm contains a variety of organelles that have different functions. New words cell - клетка independent - независимый unit - единица body - тело all - все life - жизнь human - человеческий together - вместе tissue - ткань organ systems - системы органов to function - функционировать to contain - содержать membranes - мембраны protein - протеин nucleus - ядро cytoplasm - цитоплазм different - различный Спряжение глагола to be в Present Simple. To be - быть, находиться, являться. После следующих местоимений он меняет свою форму. Спряжение глагола to be в Present Simple Таблица 1
For example. 1. I am a pupil. I am not a pupil. Am I a pupil? 2. She is a girl. She is not a girl. Is she a girl? 3. You are a good friend. You are not a good friend. Are you a good friend? Поставьте глагол to be в правильную форму, заполнив пропуски. 1. I... a pupil. 2. My father. not a teacher, he... a scientist. 3.. your sister a teacher? 4. Mary. a painter. 5.. they at home? 6. My father. a worker. 7. She. at work. 8.. you a doctor? 9. He... a pilot. 10. We... students. 11. They... carpenters. 12... they at home? 13. they... not at home. 14. He... at work. 15... your sister a typist? 16... your brother at school? 17... your sister in the cabinet? 18. My sister... at home. 19... this your cat? 20. She... an actress. 21. This... my bag. 22. He... professor. 23. Helen... a singer. 24... you an engineer? 25. He... Russian. Переведите на английский язык, употребляя глагол to be в Present Simple. 1. Я ученик. Я в школе. 2. Мой брат художник. Он не инженер. 3. Моя сестра на работе. Она врач. 4. Он студент, а не учитель. 5. Вы студент? - Нет, я ученик. 6. Моя сестра дома. Она больна. 7. Мы не в школе. Мы дома. 8. Мой брат ученик. Он в школе. 9. Ваша мама дома? - Нет, она на работе. 10. Ваш двоюродный брат дома? - Нет, он в школе. 11. Твоя сестра здорова сейчас? - Да, она здорова. 12. Ваша сестра учительница? - Нет, она студентка. 13. Твой папа на работе? Нет, он на даче. 14. Твоя сестра машинистка? - Да. Она машинистка. 15. Мой дедушка не ученый, он геолог. 16. Моя мама не учительница. Она врач. 17. Чья это ручка? - Это моя ручка. 18. Чья это книга? - Это ваша книга. 19. Чей это стол? - Это стол моего брата. 20. Чья это сумка? - Это сумка моей мамы. 21. Чей это карандаш? - Это карандаш моей сестры. 22. Это твоя тетрадь? - Да, это моя тетрадь. 23. Это тетрадь твоего брата? - Нет, это моя. 24. Где ваш стол? - Он посередине комнаты. 25. Где твоя ручка? - Она в моем кармане. 26. Где твоя тетрадь? - Она на столе. Answer the questions. 1. What is the cell consists of? 2. What is a membrane? 3. Is cell the smallest independent unit of the body? 4. What can be grown in test - tubes? 5. What can various tissues form, when they are together? 6. What are the organ system consist of? 7. What are cell characterized by? 8. What are cell organelles? 9. What ate membranes? 10. What is the cytoplasm? Make the sentences of your own using the new words (10 sentences). Find the verb to be in the text. Explain why it is used in such a way? Find one word, which is a little bit different in meaning from others (найдите одно слово, которое немного отличается от других по смыслу): 1) a) cell; b) body; c) flower; 2) a) life; b) plate; c) people; 3) a) test-tube; b) microscope; c) pen; 4) a) curtain; b) body; c) tissue; 5) a) spoon; b) kidney; c) liver. Автор: Елена Беликова << Назад: History of medicine >> Вперед: Tissue
▪ Лор-заболевания. Конспект лекций ▪ Теория бухгалтерского учета. Конспект лекций
Восприятие музыки зависит от цвета концертного зала
03.03.2026 Chrysalis: концепт межзвездного корабля для 400-летнего путешествия
03.03.2026 Дети, растущие рядом с природой, обретают крепкие кости
02.03.2026
▪ Противозачаточные таблетки влияют на чувство страха ▪ GPS-пуля ▪ Apple намерена использовать только переработанные металлы ▪ Искусственная бобровая шерсть
▪ раздел сайта Электроснабжение. Подборка статей ▪ статья Мороз и ветер. Основы безопасной жизнедеятельности ▪ статья Что такое ООО? Подробный ответ ▪ статья Медсестра. Типовая инструкция по охране труда ▪ статья Откусанный палец. Секрет фокуса
Главная страница | Библиотека | Статьи | Карта сайта | Отзывы о сайте www.diagram.com.ua |





 Смотрите другие статьи раздела
Смотрите другие статьи раздела 